- On sale!



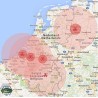
Iodine pills, which help reduce radiation build-up in the thyroid gland, had previously only been issued to people living within 20km (14 miles) of nuclear plants or dirty bomb.

Security Policy

Delivery Policy

Secure payment
Iodine pills, which help reduce radiation build-up in the thyroid gland, had previously only been issued to people living within 20km (14 miles) of nuclear plants or dirty bomb.
What is potassium iodide?
Potassium iodide is a salt, similar to table salt. Its chemical symbol is KI. It is routinely added to table salt to make it "iodized." Potassium iodide, if taken in time and at the appropriate dosage, blocks the thyroid gland's uptake of radioactive iodine and thus could reduce the risk of thyroid cancers and other diseases that might otherwise be caused by exposure to radioactive iodine that could be dispersed in a severe nuclear accident.
What is the role of potassium iodide in radiological emergency preparedness?
Potassium iodide is a special kind of protective measure in that it offers very specialized protection. Potassium iodide protects the thyroid gland against internal uptake of radioiodines that may be released in the unlikely event of a nuclear reactor accident.
The purpose of radiological emergency preparedness is to protect people from the effects of radiation exposure after an accident at a nuclear power plant. Evacuation is the most effective protective measure in the event of a radiological emergency because it protects the whole body (including the thyroid gland and other organs) from all radionuclides and all exposure pathways. Administering KI can be a reasonable, prudent, and inexpensive supplement to in-place sheltering and evacuation.
What is the benefit of taking potassium iodide during a radiological accident?
When potassium iodide is ingested, it is taken up by the thyroid gland. In the proper dosage, and taken at the appropriate time, it will effectively saturate the thyroid gland in such a way that inhaled or ingested radioactive iodines will not be accumulated in the thyroid gland. The risk of thyroid effects is reduced. Such thyroid effects resulting from radioiodine uptakes due to inhalation or ingestion, or both, could result in acute, chronic, and delayed effects. Acute effects from high doses include thyroiditis, while chronic and delayed effects include hypothyroidism, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer.
Iodine Tabelts use at a radiological accident
| Age group | Mass (mg) |
| >12 years and adults | 130 |
| 3 – 12 years | 65 |
| 1 month – 3 years | 32 |
| Neonate (< 1 month) | 16 |
In tablets of Berthelsen
| Age group | Mass (mg) |
| >12 years and adults | 570 |
| 3 – 12 years | 288 |
| 1 month – 3 years | 142 |
| Neonate (< 1 month) |
71 |
Minimum 4 pots per person recommended
Berthelsen Iodine Tabelts ingredients and normal use.
|
Content: |
Amount per daily dose (1 tablet): |
% of RDI |
|
Iodine |
225 mcg / 0.225 mg |
150 % |
This is a low dose dietary supplement. For a real disaster you need a lot of Berthelsen pots.
Ingredients:
Potassium iodide, bulking agents (maltodextrin*, microcrystalline cellulose), coating agents (silica, stearic acid, magnesium salts of fatty acids (vegetable), glycerol). *Corn, does not contain gluten.